Index Markup » Historie » Revision 9
« Zurück |
Revision 9/12
(Vergleich)
| Weiter »
Martin Kraetke, 23.12.2021 14:00
Index Markup¶
Word¶
Transpect-tex provides four methods to encode an index. They can be combined with each other.
(1) Word-Index¶
Obviously, the native Word Index feature is supported. With the \f switch, you can specify the index type.
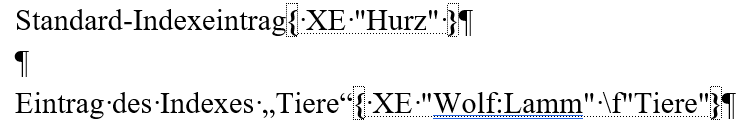
The index listing is generated based upon the marked index entries in the main text. The Word feature Insert index in the ribbon entitled References shall be used only for your own control. It is removed during the process.
If you create an index listing with Word, it does not initially contain index entries that have a certain index type with "\ f".
But here are instructions on how to create an index listing for index entries with type.
(2) Encode index entries via character style¶
You can markup phrases with a specific character style to encode them as index entry. During the conversion, an index entry is created from a phrase which has the character style ([a-z]{1,3}_index_mark). Index entries that are already encoded with the Word index feature are ignored and not encoded twice.
(3) List of index search terms¶
You can create a list of index search terms at the end of the document. During the conversion the converter searches for matches in the content and creates an index entry for each match. There are specific requirements on the list of index search terms. Each entry must have the paragraph style [a-z]{1,3}_index_list and needs to be placed in a separate paragraph. Index entries that are already encoded via Word index feature (1) or character style (2) are ignored and not encoded twice. You can also use the character style [a-z]{1,3}_index_name to mark only a part of the index search term, e.g. for John Doe, Doe can be marked so that an index entry is also created for the phrase Mr Doe.
(4) Static index¶
If you do not want to automatically search for entries in the text in the index, you can also insert a static index. You need to insert a list of index entries that yield the index_static style. Page numbers in the form of entry 144, 156, 192 are linked to the page, i.e. you have to make sure that the page reference is correct!
Index-Headings and Placement of Indices¶
You can mark individual index headings with a paragraph format (Regex: [a-z]{1,3}_index_heading). The index is rendered where the heading is in the document. Do not forget to add the index type suffix to the style name if you have multiple indices in your document.
With concordance lists and static registers, the heading must placed above the index and have the paragraph style [a-z]{1,3}_index_heading. Otherwise it won't be possible to assign the index heading to the list of index entries. For indexes with a specific type (e.g. person, location, subject etc), the type must be added to the paragraph style, e.g. [a-z] {1,3} _index_heading_person. If there is no index heading, a standard text is inserted (e.g. Index) and the index is inserted at the end of the document.
Hub XML¶
All four variants can be combined to create an index. In the hub format, index entries are given a remap attribute in the text, which they assign to a specific index:
<indexterm remap="e" type="person">
<primary>John Doe</primary>
<secondary>Great writers of Anytown</secondary>
</indexterm>For each index, an <index> element is generated. The <index> is either placed at the position of the index heading or – if not present – at the end of the document.
<index type="person" remap="e">
<title role="tsindexheadingperson">John Doe</title>
</index>
In the case of static indexes, it is assumed that the heading is always above the list of index entries. The type of index can also be specified here via an index type suffix in the paragraph style. Page numbers will be linked to the page later.
A .x_ind file is generated for static indexes during the XML conversion. In the case of dynamic indexes in the text, this must first be generated via index.sh. See below Index .
<index remap="c" type="location">
<title role="tsindexheadinglocation">Ortsregister</title>
<indexdiv>
<title>B</title>
<indexentry>
<primaryie>Bertelé, <xref xlink:href="page-93"/>, <xref xlink:href="page-94"/></primaryie>
</indexentry>
<!-- (…) -->
</indexdiv>
</index>
TeX¶
Auszeichnung multipler Indexes und deren Überschriften¶
Wir verwenden das LaTeX-Paket index für die Rohindexerzeugung, sowie Xindy zum Generieren des fertigen Registers.
Deklaration der Index-Typen¶
Das Paket erlaubt mehrere Indexe. Diese werden mit dem \(re)newindex-Befehlen deklariert:
\newindex{<typ>}{<endung rohindex>}{<endung fertiger index>}{<Überschrift>}
Damit der Skriptaufruf später korrekt funktioniert, müssen die beiden Endungen bei nicht-default-Typen dem Schema
<typ>_idx (Rohindex) bzw. <typ>_ind (fertiger Index) entsprechen.
Der Default- oder Hauptindex kriegt das Label default, dessen ÜS lässt sich wie folgt überdefinieren:
\renewindex{default}{idx}{ind}{Personenregister}
Die Index-Einträge für diesen Index werden mit
\index{<Lemma>}
deklariert. Ausgegeben wird der Hauptindex wird mit
\printindex
Angenommen, wir wollen zusätzlich zu diesem noch ein Ortsverzeichnis, dann müssen wir in der Präambel der tex-Datei einen neuen Index-Typ deklarieren:
\newindex{o}{o_idx}{o_ind}{Ortsverzeichnis}
Die Index-Einträge würden dann mit
\index[o]{<Term>}
deklariert, der Index mit
\printindex[o]
ausgegeben.
Aufruf des Index-Skripts¶
Mit dem optionalen Argument kann angegeben werden, welcher Index generiert werden soll. Wird das optionale Argument weggelassen, wird der Hauptindex erzeugt:
./index.sh <tex-Dateiname ohne Endung>
Der Aufruf mit optionalen Argument erzeugt den Neben-Index, z.B.
./index.sh <tex-Dateiname ohne Endung> o
würde das Ortsverzeichnis aus o.g. Beispiel erzeugen. Das Skript muss also für jeden Index einzeln aufgerufen werden.
Generierung des Index¶
Generieung der Indexe durch TeX¶
Heißt: Indexeinträge sind mittels \index[<typ>]{<Lemma>} in TeX kodiert.
lualatex <tex-Dateiname>.tex %% Initialer TeX-Lauf; einsammeln der ÜSen
lualatex <tex-Dateiname>.tex %% Erzeugen des IHV; seitenzahlen verschieben sich ggf.
lualatex <tex-Dateiname>.tex %% Zur Sicherheit...
./index.sh <tex-Dateiname> %% OHNE Endung!
./index.sh <tex-Dateiname> <typ> %% Zweites, optionales Argument für Index-Typ anders als default, s.u.
lualatex <tex-Dateiname>.tex %% Index wird erstmalig ausgegeben, ÜS wird geschrieben
lualatex <tex-Dateiname>.tex %% ÜS(en) für Index(e) in IHV gerendert
lualatex <tex-Dateiname>.tex %% Zur Sicherheit...
Statische Index-Dateien¶
Heißt: <basename>.<typ>_ind kommt vom Konverter
Bei statischen Indexes darf die index.sh nicht aufgerufen werden, da sonst die *ind-Dateien überschrieben würden! Alle anderen Schritte sind dieselben; \(re)newindex{}{}{}{} muss auch hier verwendet werden. Zum einen für die ÜSen, und zum anderen damit \printindex[<typ>] keine "unknown index type"-Fehler auswirft.
Von Martin Kraetke vor etwa 4 Jahren aktualisiert · 9 Revisionen